Introduction
Medicinal cannabis has emerged as one of the most talked-about developments in modern medicine. Once stigmatized and associated primarily with recreational use, cannabis is now being recognized for its therapeutic potential. Across the world, governments, scientists, and healthcare professionals are re-examining its role in treating various health conditions. This shift has led to groundbreaking research, changes in legislation, and increased public awareness of the benefits of medicinal cannabis.
In this article, we explore the factors driving the rise of medicinal cannabis, its health benefits, scientific research, legal landscape, and what the future holds for this promising plant-based therapy.
Medicinal cannabis has gained widespread recognition as a viable treatment for various health conditions, leading to its legalization in numerous countries. Once stigmatized and associated solely with recreational use, cannabis is now being embraced for its therapeutic benefits. Scientific research, changing societal attitudes, and policy reforms have played a significant role in the rise of medicinal cannabis. This essay explores the history, medical benefits, legal developments, and future potential of medicinal cannabis in healthcare.
The Historical Perspective
Cannabis has been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years. Ancient civilizations, including those in China, Egypt, and India, utilized cannabis to treat pain, inflammation, and various ailments. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, cannabis extracts were widely used in Western medicine. However, with the rise of drug prohibition in the 20th century, cannabis was classified as an illegal substance, halting its medical applications for decades. It was not until the late 20th and early 21st centuries that researchers began to reevaluate its medicinal potential, leading to a resurgence in its acceptance.
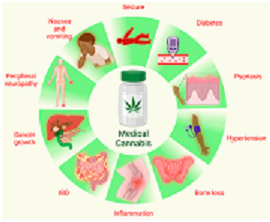
Health Benefits of Medicinal Cannabis
1. Pain Management
.Chronic pain affects millions of people worldwide, often leading to a dependency on opioids. Medicinal cannabis has been shown to provide relief for pain associated with arthritis, neuropathy, and migraines. Unlike opioids, cannabis has a lower risk of addiction and overdose.
2. Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
One of the most well-documented medical uses of cannabis is in treating epilepsy. CBD-based medications like Epidiolex have been approved for treating rare forms of childhood epilepsy, significantly reducing seizure frequency.
3. Anxiety and Depression
CBD has been found to have anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) properties. Many patients with generalized anxiety disorder, PTSD, and depression have reported improvements in mood and stress management when using medicinal cannabis.
4. Cancer Symptom Relief
Cancer treatments such as chemotherapy often cause nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. Medicinal cannabis has been shown to alleviate these side effects, improving the quality of life for cancer patients.
5. Neurodegenerative Diseases
Cannabis’s anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties make it a potential treatment for conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. Research indicates that cannabis may help slow the progression of these diseases and ease symptoms like muscle spasticity and tremors.
6. Sleep Disorders
Cannabis has been used to promote sleep in patients suffering from insomnia or sleep apnea. Certain strains, especially those with a high CBD-to-THC ratio, can help regulate sleep cycles.
Countries Leading the Way:
- Canada: Legalized both medical and recreational cannabis.
- United States: Many states have legalized medicinal cannabis, with the FDA approving cannabis-based medications.
- Germany: Patients can obtain medicinal cannabis through prescription.
- Australia: Legalized for medical use, with growing accessibility.
- Israel: A pioneer in cannabis research and medical applications.
As more clinical studies confirm cannabis’s benefits, governments are beginning to reconsider outdated laws, creating a more favorable environment for its use.
"Scientific studies have demonstrated that cannabis contains compounds called cannabinoids, which interact with the human body's endocannabinoid system to regulate pain, mood, and other physiological functions. Two key cannabinoids—tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD)—have been widely studied for their medicinal properties."
Legalization and Policy Changes
Over the past few decades, numerous countries and states have reformed their cannabis laws, recognizing its medicinal benefits. The United States, Canada, Germany, Australia, and many others have legalized medicinal cannabis, allowing patients to access cannabis-based treatments through prescriptions. Legalization has led to increased funding for research, improved product quality, and better regulation to ensure patient safety. However, despite its growing acceptance, medicinal cannabis remains controversial in some regions due to concerns about misuse, addiction, and regulatory challenges. Policymakers continue to balance the need for patient access with the need for controlled distribution and oversight.
Challenges of Medicinal Cannabis
Despite its promising future, medicinal cannabis still faces significant challenges:
1. Regulatory Hurdles
Governments have strict regulations surrounding the production, distribution, and prescription of cannabis. The varying laws across different regions create confusion and limited access for patients.
2. Lack of Standardization
Unlike pharmaceutical drugs, cannabis products often lack standardization in dosage and potency. This inconsistency makes it difficult for doctors to prescribe with precision.
3. Stigma and Misinformation
Even with growing acceptance, the stigma around cannabis use persists. Many people remain skeptical about its benefits due to decades of misinformation.
4. Cost and Accessibility
In some regions, medicinal cannabis remains expensive and inaccessible to patients who need it most. High production costs, taxes, and regulatory fees contribute to these barriers.
The Future of Medicinal Cannabis
The medicinal cannabis industry is evolving rapidly, with ongoing research uncovering new applications. Here are some expected developments:
1. Improved Pharmaceutical-Grade Cannabis Medications
Pharmaceutical companies are investing in research to develop more precise cannabis-based treatments, ensuring consistent dosing and targeted effects.
2. Expanding Legalization
As more clinical evidence supports cannabis’s benefits, we can expect more countries to legalize or decriminalize its use for medical purposes.
3. Integration with Mainstream Medicine
More medical professionals are incorporating cannabis into treatment plans, leading to better education and awareness in the healthcare sector.
4. Personalized Cannabis Medicine
With advances in genetic testing and personalized medicine, future cannabis treatments may be tailored to an individual’s unique biochemistry, maximizing effectiveness.
The rise of medicinal cannabis represents a major shift in healthcare, moving from stigma and prohibition to acceptance and scientific validation. Its ability to alleviate pain, treat neurological disorders, and support mental health has made it an important alternative treatment for many medical conditions. While challenges remain, the growing body of research and policy reforms indicate that medicinal cannabis will continue to play a significant role in modern medicine. As awareness increases and regulations evolve, more patients will have access to this natural and effective form of treatment, ultimately improving lives and shaping the future of healthcare.
Back to Home
Leave a Comment